Statement of Retained Earnings: A Complete Guide Bench Accounting

A growing balance suggests an emphasis on expansion, while a declining balance may indicate financial distress or aggressive dividend policies. Analysts examine this balance to evaluate a company’s growth potential and financial strategy. Retained earnings can typically be found on a company’s Accounting For Architects balance sheet in the shareholders’ equity section. Retained earnings are calculated through taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding to the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts.
- A business entity can have a negative retained earnings balance if it has been incurring net losses or distributing more dividends than what is there in the retained earnings account over the years.
- These earnings are typically also used for growth, but they’re not earmarked for a specific transaction or project.
- While it’s sometimes referred to as the statement of stockholders’ equity, statement of owner’s equity, or equity statement, these technically aren’t the same thing.
- Here we can see the beginning balance of its retained earnings (shown as reinvested earnings), the net income for the period, and the dividends distributed to shareholders in the period.
- Retained earnings are that part of a firm’s profits which is not distributed as dividends to shareholders.
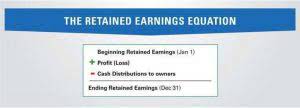
Statement of Retained Earnings Formula

The net income of a business belongs to the owners, we have seen above that the net income can either be paid out to the owners by way of dividend, or kept within the business, as retained earnings. Either way, the net income and therefore the retained earnings, belongs to the owners and forms part of the owners equity. The retained earnings for each year accumulate on the Retained Earnings account which forms part of the owners equity in the balance sheet. Retained earnings refers to the net income retained by a business after any distribution (dividends) to the equity holders. In effect the net income is split between the amount paid out to equity holders and the amount retained within the business.

Common mistakes to avoid when calculating retained earnings
The retained earnings statement is one of the four main financial statements and is the link between the income statement and the balance sheet. Sum up the figures added to the statement of retained earnings to calculate the closing balance. This will be the amount of retained earnings reported on the current period’s balance sheet in the shareholders’ equity section. Investors who have invested in a Company gain either from dividend payments or the share price increase. In contrast, a growing Company is expected to retain the income and invest in future business, thus expecting an increase in the share price.
Retained Earnings vs. Dividends
Companies may pay out either cash or stock dividends, and in the case of cash dividends they result in an outflow of cash and are paid on a per-share basis. Generally, companies like to have positive net income and positive retained earnings, but this isn’t a hard-and-fast rule. The decision to pay dividends or retain earnings for future capital expenditures depends on many factors. Changes in accounting estimates, such as cash flow depreciation methods or inventory valuation, are applied prospectively, affecting only current and future financial statements. Clear disclosure of these adjustments in financial statement notes provides stakeholders with context and justification. Adjustments for accounting changes ensure the accuracy of financial reporting.
What Are Private Goods? Definition, Examples, and Key Accounting Factors
Both cash dividends and stock dividends result in a decrease in retained earnings. The effect of cash and stock dividends on the retained earnings has been explained in retained earnings statement the sections below. Understanding the retained earnings statement is crucial for analyzing a company’s financial health. This document reveals how much profit has been reinvested in the business rather than distributed as dividends, offering insights into growth potential and stability. Dividends, the portion of earnings returned to shareholders, directly reduce retained earnings. Dividend policies reflect a company’s financial health and investment strategy.

Retained earnings are reported under the equity section of a company’s balance sheet. If a company accumulates more net losses than net profits over the years, then it can have negative retained earnings. The portion of its earnings that a company does not distribute as dividends to shareholders is known as retained earnings.


Cevapla
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!